Recently, The team of Professor Wang Guifang from SKL is entitled "Effect of polyelectrolyte structure on perchlorate adsorption performance by functionalized montmorillonite" was published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
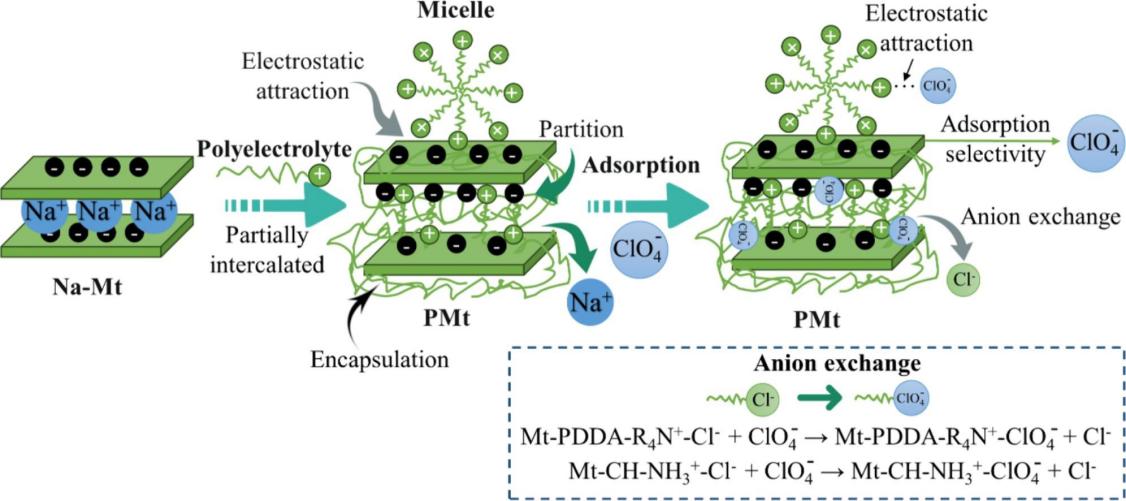
Polyelectrolyte (with different unit structure or molecular weight) modified montmorillonite (PMt) was synthesized for perchlorate (ClO4-) removal. It was found polyelectrolytes were successfully loaded on montmorillonite (Mt), and the surface potential of most PMt changed from negative to positive. Polyelectrolyte desorption on Mt was < 10 % after 48 h. Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) species modified montmorillonite (PDDAx-Mt) showed excellent adsorption performance for ClO4-with maximum adsorption amount over 2.78 mmol/g and equilibrium time within 10 min. The adsorption performance of PMt toward ClO4- followed this order: PDDAx-Mt > CH-Mt > PAM-Mt > PQ28-Mt. Moreover, PDDAx-Mt and CH-Mt showed a superior adsorption selectivity to ClO4- among competitive oxyanions in the quaternary-adsorbate system (ClO4- > PO43- > SO42- > NO3–). The enhanced ClO4- adsorption could be mainly attributed to the presence of anion exchange sites (−R4N+-Cl− or –NH3+-Cl−) provided by PDDA or CH, followed by electrostatic gravitation and weak hydrogen bonding interaction. Density functional theory (DFT) calculation revealed that ClO4- adsorbed on PMt is a process of electrons transferring from O atoms in ClO4- to H atoms on C in PDDA+ or N in CH+, PAM+ and PQ28+. The preparation method of PMt is simple with excellent adsorption performance and selectivity toward ClO4-, suggesting promising applications in anion wastewater treatment.