In July 2024, The team of Professor Wang Xinpeng from SKL is entitled "Facile one-pot in-situ hydrothermal preparation of 0D/2D Mn3O4/CdS heterojunctions for improved photocatalytic H2production and degradation of methylene blue" was published in the Surfaces and Interfaces.
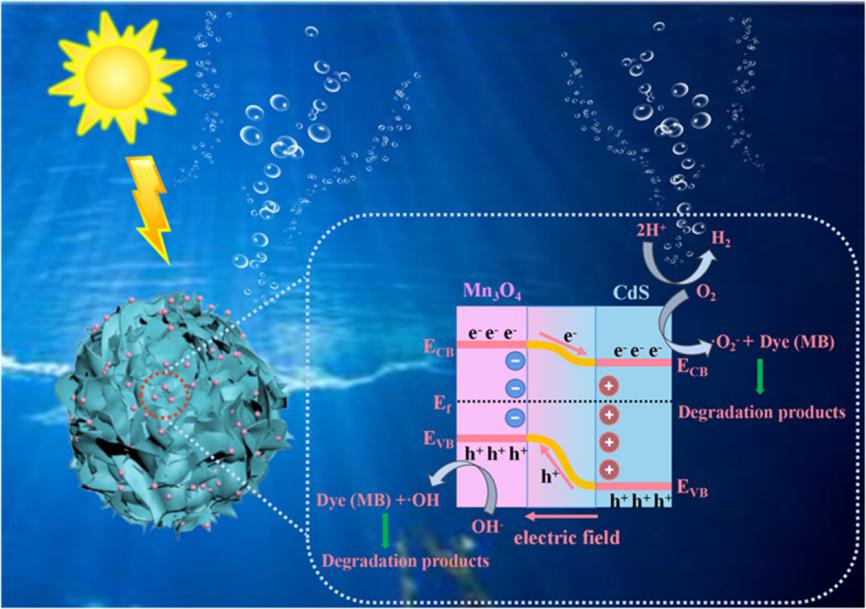
Developing heterojunction photocatalysts is a critical method to augment the photocatalytic activity of single semiconductors. However, the instability of their heterostructure poses a significant challenge. Herein, a unique 0D/2D Mn3O4/CdS p-n photocatalyst has been prepared by a simple one-pot in-situ hydrothermal approach for H2production and methylene blue (MB) degradation. The optimized MC-0.18 (18 at% Mn) nanocomposite showed remarkable photocatalytic properties, producing a significantly higher H2 generation rate of 1291 μmol·g−1·h−1, which was 13.7 and 9.2 times higher than that of pristine CdS and ex-situ synthesized MC-0.18-ex photocatalysts, respectively. MC-0.18 displayed the highest reaction rate at 0.0435 min−1 for MB degradation, which was approximately 2.6 and 6.3 times higher than CdS and Mn3O4, respectively. Active species capture experiments and ESR identified •OH and •O2− as the main substances involved in MB degradation. Importantly, MC-0.18 demonstrated excellent stability and reusability in photocatalytic H2production and MB degradation cycle tests. The formation of unique p-n heterostructures results in enhanced photoactivity due to the matched band alignment between ultrafine Mn3O4nanoparticles and CdS nanosheets, leading to a high charge separation capacity. This study offers a facile route to design p-n heterojunctions that have remarkable charge transfer abilities to promote H2 production and degrade organic dyes.